Affordable Housing Trends in india remains a key segment in India’s real estate market due to rising incomes and an increase in desire for homeownership; additionally, this segment presents attractive investment opportunities.
Policy reforms and financial incentives are helping make housing more accessible and affordable in India, including initiatives like Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana and home loan interest subsidies that make owning property more attainable for potential buyers.
Demand for affordable housing trends in key metros
Demand for affordable housing in key metros such as Chennai, Delhi-NCR, Hyderabad, Mumbai and Ahmedabad is on the rise. Rising incomes have contributed to this rise, however due to limited supply in these areas there remains limited capacity of such properties available at affordable costs – hampering further development in these cities.
An important contributor to this trend is the high cost of land, infrastructure development and government policies, which is pushing up real estate prices faster than wage or inflation growth – thus rendering luxury homes in top cities out of reach for many middle-income households.
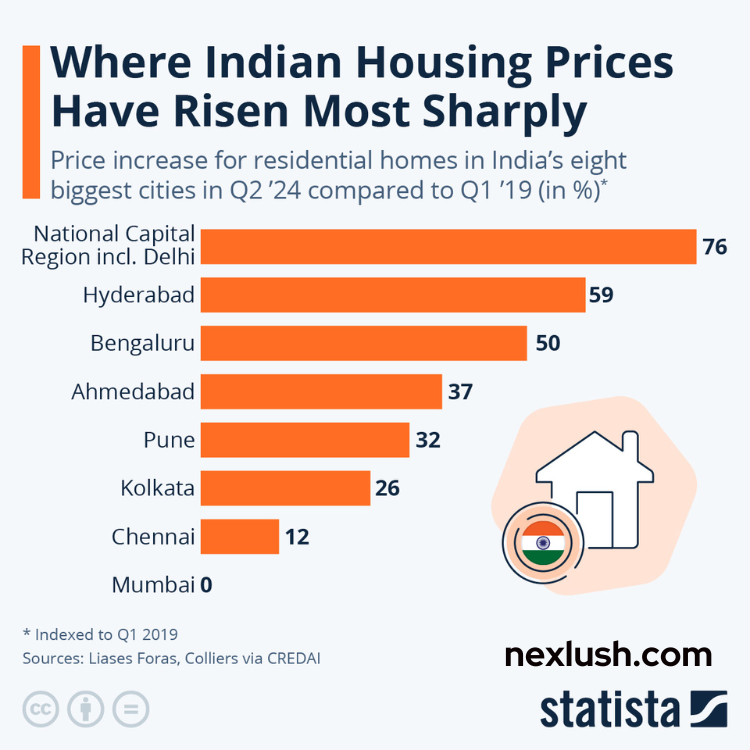
Home affordability has increased in eight cities, yet Mumbai and New Delhi-NCR remain outside the affordable threshold. The Knight Frank India Home Affordability Index 2023 shows that households living there must spend over 50% of their income on loan EMIs to remain affordable.
Situation is further compounded by the fact that affordable housing projects tend to be located in peripheral areas, far from workplaces, schools and hospitals as well as lacking adequate infrastructural facilities – this distance often dissuades buyers and reduces occupancy rates. To address this issue, government is offering tax benefits and faster approval times as incentives for developers who build affordable housing in these locations – this will enhance quality while increasing supply of such projects.
Demand in North India
North India’s demand for Affordable Housing Trends is being driven by rapid urbanization, population growth and migration into urban areas. Unfortunately, availability remains limited due to supply constraints and financing issues; nevertheless demand is expected to remain strong as populations increase and incomes grow – as well as rising nuclear family trends that further necessitate affordable homes.
Covid-19 pandemic also severely undermined consumer confidence levels and drove mortgage rates higher, prompting some prospective buyers to postpone making purchases decisions. Rising construction costs reduced margins for affordable housing developers; as a result, they increasingly turned towards luxury segments, where higher profit margins existed.
An additional hurdle lies in urban centers and suburban areas’ lack of adequate infrastructure, which impedes affordable housing project development and access, forcing many households into informal settlements or slums. Furthermore, land acquisition costs and lengthy approval processes exacerbate project timelines and costs significantly.
Government efforts to promote affordable housing include subsidies and incentive schemes that help ease homebuyer financial strain and encourage developers to invest in this sector. State-specific policies and incentives also complement central initiatives by increasing affordability for urban residents; sustainable building practices as well as inclusive design can further add livability.
Challenges in key metros
As India continues to urbanize, demand for affordable housing increases, but supply does not. Therefore, finding innovative solutions to increase affordability has become ever more urgent; in response, government incentives for developers have been introduced while expanding access to these properties in key cities.
Rising household incomes and their desire to own homes is creating an increase in demand for more affordable properties in key cities across India. This trend can be seen particularly clearly in metros such as Chennai, Kolkata, Hyderabad and Delhi-NCR, where family income-to-EMI ratio is under 50%; however affordability remains an obstacle in cities like Mumbai and Gurugram.
According to MagicbricksPropIndex reports, property prices in these areas have exceeded general inflation and wage growth significantly – making luxury housing unaffordable for many in these cities while pushing up land and construction costs.
Demand for Affordable Housing Trends is driven by migration from villages and small towns into cities for employment and education opportunities, many seeking houses that provide them with security close to work. Furthermore, digital technologies have led to remote work opportunities which has given people greater flexibility regarding where they choose to reside; as a result, preferences have shifted toward homes featuring designated workspaces with reliable Internet connectivity as an economical housing option.
Challenges for Affordable Housing Trends in North India
Affordable Housing Trends requires significant investments, yet government initiatives and financial support alone cannot ensure its development. Land acquisition costs and regulatory bottlenecks can significantly increase project costs and limit affordable housing development; these obstacles may be mitigated with effective collaborative efforts and transparent legal reforms.
Rapid urbanization and demographic shifts in India are fuelling a surge in affordable housing demand. More Indians have moved from villages into cities, leading to greater density in these locations as well as a surge in compact and affordable homes in convenient spots. Meanwhile, nuclear family households are altering household dynamics and spurring smaller home sizes; developers and real estate firms have responded by creating more accessible projects that meet this need.
The Government of India has initiated several policies and schemes designed to support affordable housing development in urban centers. One such scheme, Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana, offers interest subsidies on loans made available for economically weaker sections and low-income groups, making homeownership more accessible for many families. Furthermore, special financing schemes have also been established so developers can secure long-term funding for such projects.
North India’s affordable housing market faces numerous hurdles, such as funding constraints and regulatory restrictions. Infrastructure deficiencies impede accessibility of affordable housing projects and impact residents’ quality of life; additionally, community resistance may cause delays to affordable housing projects being built.
Must Read: Shoe Balancer Height Increase
[…] Must Read: Affordable Housing Trends […]